Open House
Global Warming
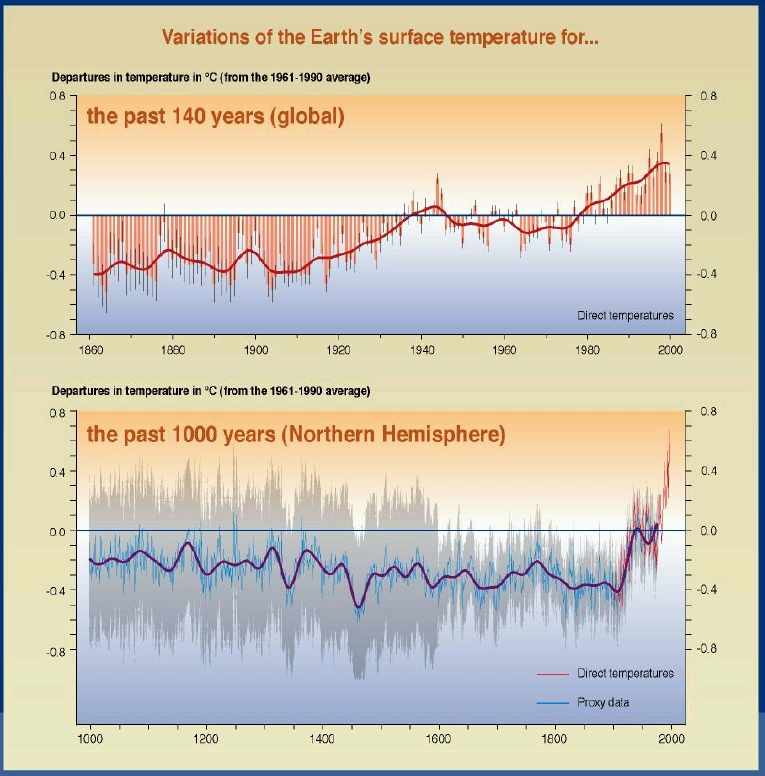
Scientists estimate that mean global temperatures have increased by
0.5 to 1.0 °F (0.3 to 0.6 °F) in the last 100 years (Figure 1). Note that this
is an increase in the "mean global" temperature. "Mean global
temperature" refers to the average of all of the temperature changes
from throughout the world. In reality, the temperature change has
not been consistent across the planet.
In fact, the temperature change has not been consistent in time.
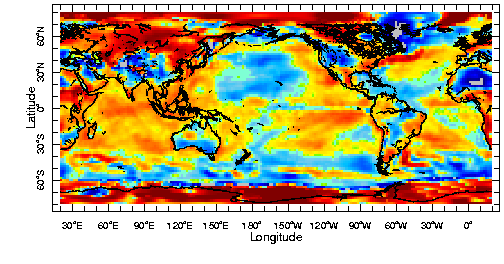
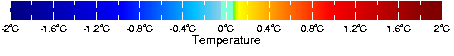
1990s-1970s
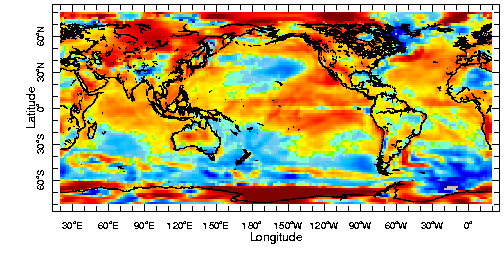
|
1990s-1960s
|
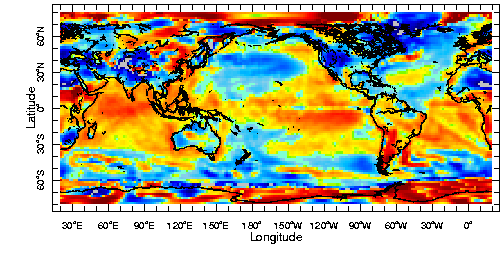
1990s-1950s
|
|
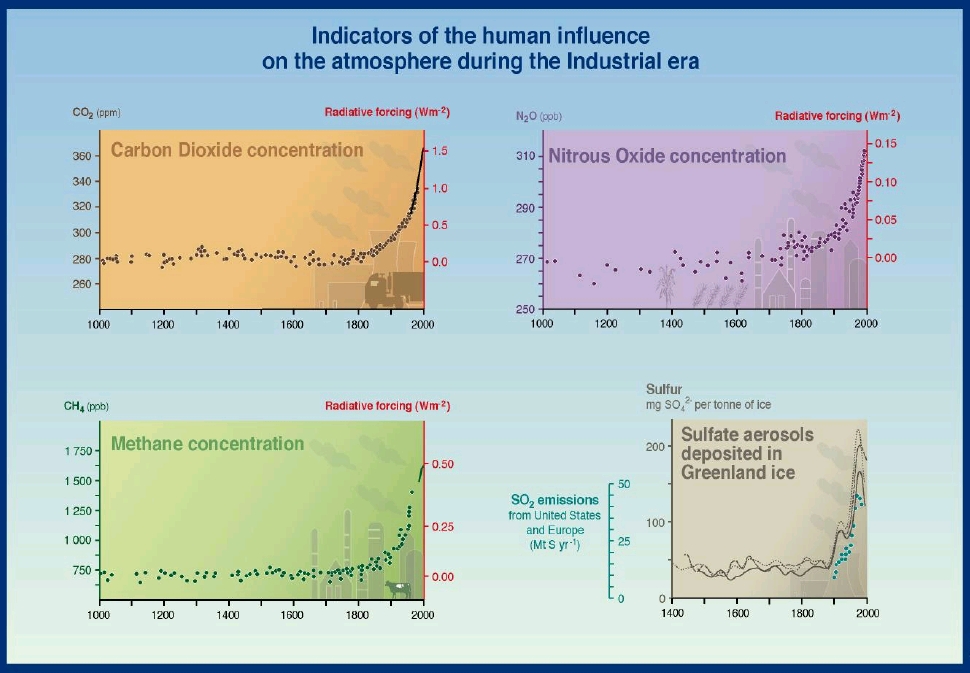
Increased levels of carbon
dioxide in the atmosphere (Figure 2)
would tend to warm the surface of the earth. But the increased levels
of sulfate aerosols (acid rain) (Figure 2)
tend to cool the surface of the earth.
Sulfates can scatter the sun's light before it reaches the earth's surface.
Without heat from the sun, the earth's surface will cool. Ironically,
those regions which have managed to use new technologies to reduce
emissions of sulfur dioxide (using "scubbers" and low-sulfer fuels)
are now starting to feel the full effects of increased CO2.
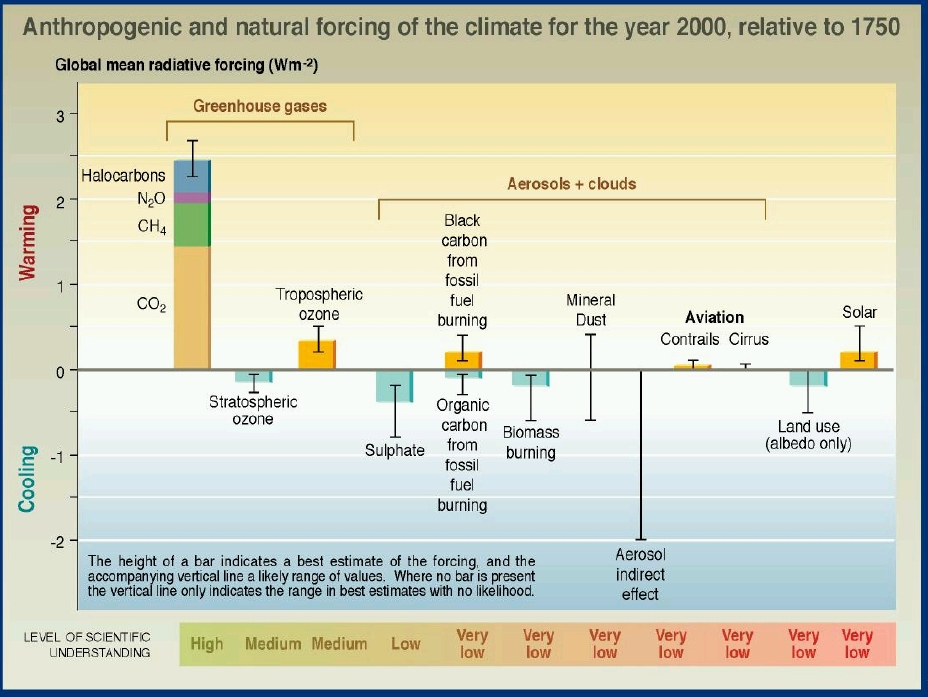
For more information about which pollutants warm the surface
temperature, and which cool the surface temperature see (Figure 3).
Activity: The 1990s minus the 1950s/60s/70s
Pick a region and decades, then click on "plot" to see the difference in surface temperature.
Figures from IPCC-2001